Boolean Algebra in Digital Systems and Computing
Discover how Boolean Algebra powers modern computing — from processors and memory to control logic and programming.
Advanced
30 min
Throughout this course, you’ve learned how Boolean algebra provides a formal, mathematical way to describe and manipulate logic. Now, in this final lesson, we’ll bring everything together to explore how Boolean logic powers the digital world. From the physical circuits inside your computer to the logical expressions in programming languages, Boolean operations are everywhere. In fact, nearly all digital systems — including the device you’re reading this on — rely on Boolean algebra at their core.
This lesson shows you how the abstract rules and structures you’ve studied are translated into real, working systems. You’ll see how Boolean expressions control circuits, shape software decisions, and enable everything from web searches to artificial intelligence. Understanding this connection is crucial for anyone pursuing computer science, electrical engineering, or even high-level software development.
Introduction
Boolean algebra isn’t just an academic exercise or an obscure form of logic — it’s the language of the digital age.
When engineers design a processor, they aren’t writing paragraphs of prose or drawing pictures. They’re creating precise arrangements of logic gates, each one performing Boolean operations like AND, OR, or NOT. These gates are wired together based on Boolean expressions that determine how a device processes data, makes decisions, or performs calculations.
Here are just a few places where Boolean algebra is actively used every day:
- Processors (CPUs) use Boolean logic to perform arithmetic, evaluate conditions, and make branching decisions.
- Memory systems rely on Boolean-controlled circuits like flip-flops and latches to store and manage bits.
- Programming languages implement Boolean operators (
&&,||,!) to control the flow of logic in software. - Networking systems use Boolean rules to allow or block traffic, filter data, or route packets.
- Search engines use Boolean logic to match and prioritize information based on queries.
Without Boolean algebra, there would be no digital logic, no computing, and no modern information systems. Every digital system — whether simple or complex — can ultimately be described by a network of logic gates guided by Boolean expressions.
In this lesson, we’ll explore this integration between theory and practice by looking at how Boolean algebra is embedded in:
- Hardware circuits (processors, memory, controllers)
- Programming and software logic
- Simulation and circuit design tools
- Real-world applications like AI, networking, and automation
By the end, you’ll understand why Boolean logic is not only foundational but also universal — an invisible framework behind nearly every modern technology.
Great! Let’s now continue with the next section of Lesson 14, which focuses on how Boolean Algebra is applied in digital hardware design — the physical layer where logic comes to life.
Boolean Algebra in Hardware Design
At the heart of every digital system is hardware logic — circuits made from transistors wired together to
form logic gates. These gates implement Boolean operations in physical form. A Boolean expression such as A · ¬B + C
isn’t just a theoretical formula; it translates directly into a real-world configuration of electronic components.
Logic Gates
Every logic gate you’ve studied — AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR — is constructed from transistors, typically using CMOS technology. Gates can be connected in networks to perform any Boolean function, no matter how complex. For example:
- The Boolean expression
A · Bis realized as a simple AND gate with two inputs. - The expression
¬(A + B)can be implemented using a NOR gate.
These gates are the basic building blocks of combinational logic circuits — circuits whose outputs depend only on current inputs.
Components Built with Boolean Logic
Using combinations of logic gates, engineers build larger functional units. Here are some key digital components directly designed using Boolean algebra:
-
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU):
- Performs arithmetic and logical operations inside a CPU
- Operations like ADD, SUB, AND, OR are built from Boolean circuits
- Example: An adder circuit uses combinations of XOR, AND, and OR gates
-
Multiplexers (MUX):
- Use selection bits to choose between inputs
- Boolean logic defines the conditions under which each input is passed to the output
-
Decoders & Encoders:
- Translate binary values into signals for control or display
- Designed using SOP or POS logic expressions
-
Memory Elements (Flip-Flops, Latches):
- Store bits using feedback and control logic
- Boolean expressions define the conditions for writing, reading, and resetting memory
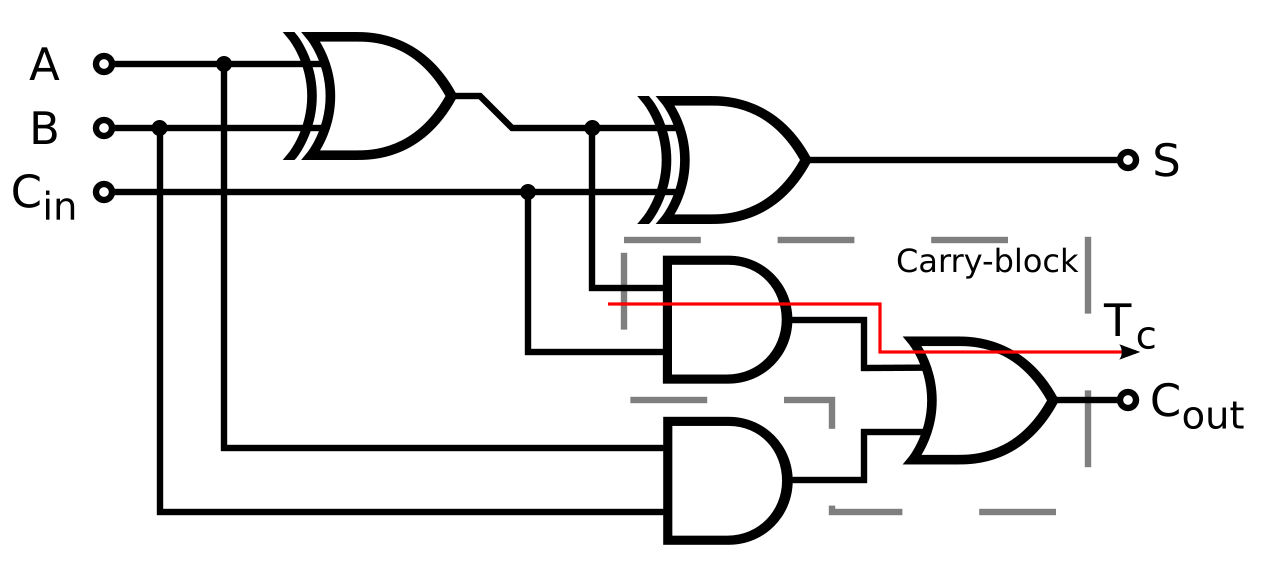
Example: Designing a 1-Bit Full Adder
A full adder adds two binary digits plus a carry-in and outputs a sum and carry-out.
Boolean equations:
- Sum = A ⊕ B ⊕ Cin
- Carry = (A · B) + (Cin · (A ⊕ B))
This design uses:
- XOR gates for the sum
- AND and OR gates for the carry
This real circuit behavior comes directly from Boolean expressions and can be implemented physically with logic gates in chips.
In short, Boolean algebra serves as the blueprint for digital hardware. Any function you want a circuit to perform must first be expressed using Boolean logic — and then translated into gates and wiring. It’s the bridge between abstract logic and physical electronics.
Great! Let’s now explore how Boolean algebra extends beyond hardware and into the world of software, powering logic in programming languages, algorithms, and everyday code execution.
Boolean Logic in Programming and Algorithms
While Boolean logic forms the physical core of digital systems, it’s just as critical in software development.
Programmers use Boolean expressions to make decisions, control the flow of programs, and implement algorithms.
Every if statement, every loop condition, and every logical comparison you write relies on Boolean evaluations
behind the scenes.
Boolean Expressions in Code
In most programming languages, Boolean logic is implemented through:
-
Logical operators:
AND:&&orandOR:||ororNOT:!ornot
-
Relational expressions:
==,!=,<,>,<=,>=— all return Boolean values (trueorfalse)
These expressions combine to form logic that determines the flow of a program.
Example (Python):
if (age >= 18 and has_id):
print("Access granted")This condition uses a Boolean AND to decide if both criteria are met.
Boolean Logic in Control Flow
Control structures — like if, while, for, and switch — depend entirely on Boolean values:
if condition:→ run code only if the condition evaluates to truewhile condition:→ loop while the condition remains true
Example (JavaScript):
while (temperature > 100 && systemRunning) {
coolDown();
}The loop runs only if both conditions are true.
Boolean Logic in Algorithms
Algorithms often rely on Boolean expressions to:
- Control iterations and recursion
- Decide which path to follow (branching)
- Compare search conditions (e.g.,
x in list) - Filter data (e.g.,
filter(lambda x: x > 10 and x < 50))
Example: Binary Search Condition
if target < array[mid]:
right = mid - 1
else:
left = mid + 1Here, each step in the algorithm depends on a Boolean condition evaluating the relationship between elements.
Short-Circuit Evaluation
Most modern programming languages use short-circuit logic:
- In
A && B, ifAis false,Bis never evaluated - In
A || B, ifAis true,Bis skipped
This is both a performance optimization and a way to avoid errors (e.g., checking object != null && object.property).
Boolean Types and Logic in Data Structures
- Languages like Python, C, and Java include a
booltype (trueorfalse) - Data structures like filters, sets, and maps often rely on Boolean conditions for inclusion, search, or updates
Example (C):
bool isEven(int x) {
return (x % 2 == 0);
}Boolean logic gives programming structure, control, and flexibility. Every conditional path a program takes — every decision — is ultimately the evaluation of a Boolean expression. In that sense, writing code is much like building logic circuits: you’re defining how the system reacts to different inputs.
Modern Applications of Boolean Logic
Boolean algebra is embedded into the core logic of modern computing systems, including artificial intelligence, networking, databases, and automation. Its principles enable machines to make decisions, filter data, and respond to dynamic inputs — all based on logical expressions that return true or false.
Let’s look at some practical domains where Boolean logic is crucial:
1. Artificial Intelligence and Decision Systems
In rule-based AI systems, Boolean logic is used to express decision trees and expert rules:
-
Conditions like
IF temperature > 30 AND humidity < 50 THEN activate cooling systemare broken into logical tests using AND, OR, and NOT. -
Logic-based AI frameworks (such as Prolog) depend entirely on Boolean truth evaluations to reason over knowledge bases.
-
Even in machine learning, decision tree classifiers use binary (Boolean) splits on data:
- “Is
age < 18? Yes → Left branch; No → Right branch.”
- “Is
Boolean logic allows AI systems to reason, filter, and classify inputs in a transparent and controllable way.
2. Network Security and Firewalls
Firewalls and routers use Boolean logic to enforce security policies:
-
Rules like:
ALLOW traffic IF (IP == 192.168.1.10 AND port == 443)BLOCK IF (source = unknown OR protocol = UDP)
These rules are implemented as chains of Boolean conditions checked for each packet. If a condition evaluates as true, the system allows or blocks the traffic accordingly.
Routers, intrusion detection systems, and access control software all rely on Boolean logic to make real-time, high-speed decisions.
3. Search Engines and Databases
When you type into a search bar or query a database, Boolean logic silently goes to work.
-
Search engines interpret logical operators in queries:
climate AND policy("climate change" OR "global warming") AND Brazil NOT deforestation
-
SQL databases filter rows using Boolean WHERE clauses:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE (age > 18 AND country = 'Brazil') OR admin = true;
These queries are compiled into logic trees where each branch is a Boolean expression evaluated row-by-row or document-by-document.
Boolean algebra makes it possible to narrow, refine, and structure information retrieval in massive datasets.
4. Robotics and Automation
In automation systems (like factories or smart homes), Boolean logic is used to control devices based on input sensors:
IF motion_detected AND time > 18:00 THEN turn_on_lightsIF door_open AND alarm_armed THEN trigger_siren
Industrial PLCs (programmable logic controllers) run programs that are essentially Boolean instruction lists, processing real-time conditions through logic gates.
Robots also use Boolean logic for pathfinding decisions, obstacle avoidance, and task execution.
Certainly! Here’s the final section of Lesson 14, wrapping up everything with a summary and suggestions for further learning.
Key Takeaways
Throughout this course, you have explored the fundamental principles of Boolean algebra, starting from its basic definitions and operations, advancing through simplification techniques, standard forms, and finally understanding its pivotal role in digital systems and computing.
In this last lesson, we connected the dots between abstract Boolean expressions and their practical applications in hardware design, CPU and memory operations, programming logic, simulation tools, and modern technology domains such as AI, networking, and automation.
- Boolean algebra underpins the very fabric of all digital electronics, enabling precise control over electrical signals to perform computations and store data.
- CPUs and memory rely on Boolean logic to process instructions and manage information flow.
- Programming languages incorporate Boolean logic to control decision-making and program flow.
- Simulation tools and HDLs translate Boolean logic into physical hardware implementations.
- Real-world technologies—from artificial intelligence to networking security—depend heavily on Boolean logic to function effectively.
Next Steps
If you’re excited to deepen your knowledge, consider exploring these topics:
- Binary Number Systems and Arithmetic: Understanding how numbers are represented and calculated in digital circuits.
- Sequential Logic and State Machines: Learn about circuits that depend on previous states, such as flip-flops, counters, and registers.
- Logic Minimization and Karnaugh Maps: Master techniques to simplify complex logic expressions for efficient hardware.
- Hardware Description Languages (HDLs): Gain skills in VHDL or Verilog for describing and simulating hardware.
- Digital System Design and FPGA Programming: Apply your knowledge to program real hardware devices and prototype digital circuits.
- Introduction to Computer Architecture: Explore how Boolean logic integrates into processor design, memory hierarchy, and system buses.